Key takeaways
- The human body has 206 bones, which form the bony framework of the body.
- The skeletal system is responsible for supporting and giving shape to the body, protecting vital organs, and providing sites of attachment for muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- Osteology is the study of the structure of bones.
- Bones are made up of inorganic mineral salts and an organic substance called ossein.
- The bones of the human skeleton provide rigid support, protect vulnerable organ systems, and serve as a repository for calcium and phosphorus.
- Bones have a hard outer shell, called compact bone, and an inner spongy, porous portion, called cancellous tissue.
- The ends of long bones have smooth and glossy tissue that forms the joint surfaces, known as articular cartilage.
- The thin outer membrane surrounding bones is called the periosteum, which plays an important role in supplying blood and nutrients to the bone and is also the pain center of bones.
- There are two types of bone marrow: yellow, which is composed of fat cells, and red, which is a manufacturing center for red blood cells.
- The skeletal system works in concert with other body systems, including muscles, to maintain overall health and well-being.
Introduction
The skeletal system is a complex network of bones that forms the bony framework of the human body. It is made up of 206 bones and holds the body together and gives it shape.
It also protects vital organs and gives muscles, tendons, and ligaments places to attach.
To understand how the skeleton works with muscles to provide support and movement, you need to know how bones are made and what they do.
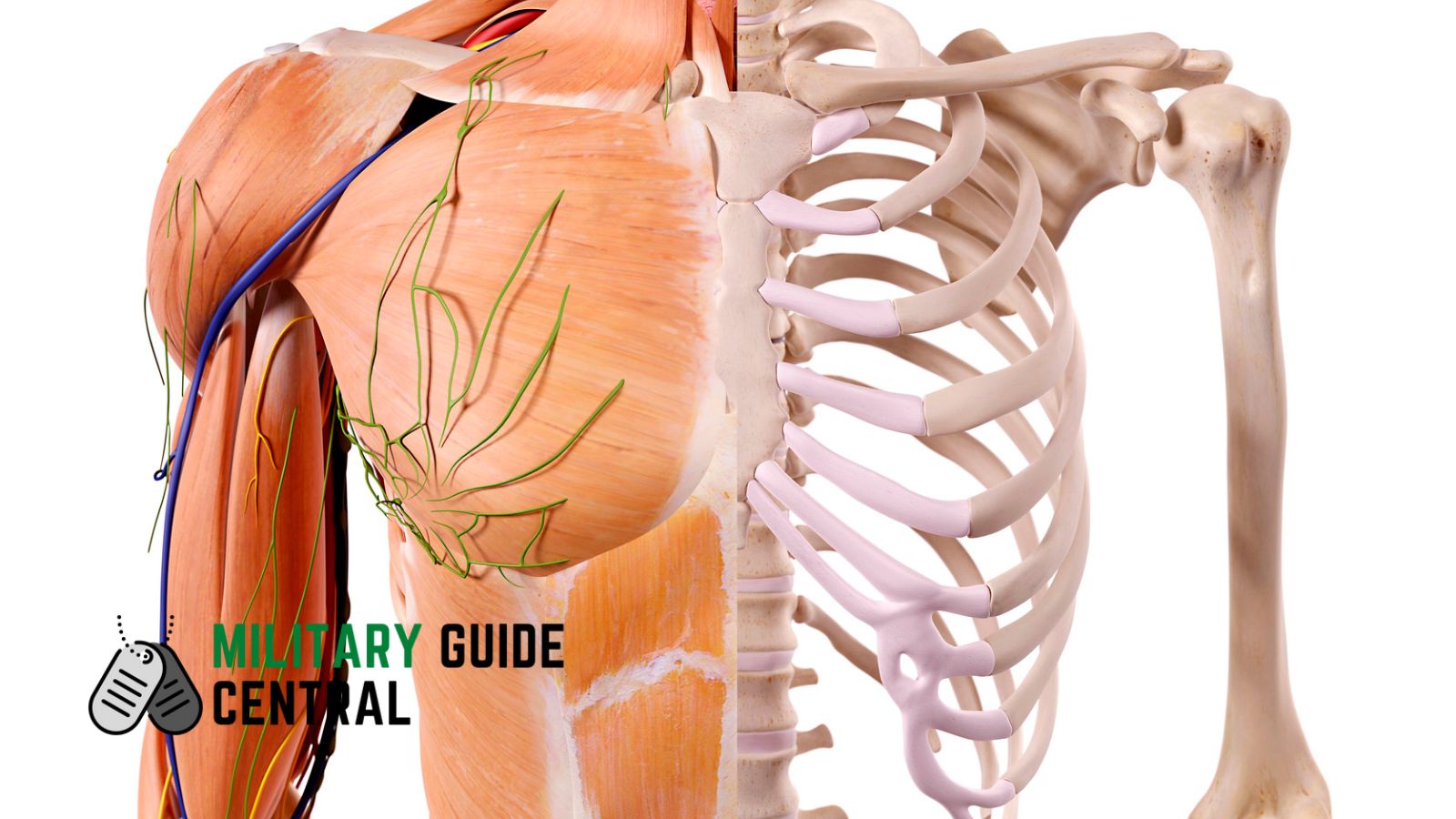
Anatomy of Bones
Osteology is the study of the structure of bones and their composition. Bones are made up of inorganic mineral salts and an organic substance called ossein.
Mineral salts give bones their strength and hardness, while cells and fibers of connective tissue make up the organic part.
The bones of the skeleton give the body structure and protect organs that aren’t as strong. They also store calcium and phosphorus, two minerals that the body needs.
Structure of Bones
Bones have a hard outer shell, called compact bone, and a spongy, porous portion inside, called cancellous tissue.
The center of the bone is the medullary canal, which contains bone marrow. There are two types of bone marrow: yellow, which is composed of fat cells, and red, which is the manufacturing center for red blood cells.
Joint Surfaces
The ends of long bones have smooth, glossy tissue that forms the joint surfaces, known as articular cartilage. This tissue makes it possible for bones to move together or fit into other bones with similar surfaces.
Periosteum
The thin outer membrane surrounding bones is called the periosteum.
It plays an important role in supplying blood and nutrients to the bone, as capillaries and blood vessels run through it and into the bone surface. The periosteum is also the pain center of the bones.
Conclusion
In the end, the skeletal system is a complicated and important part of the human body that helps support, protect, and move the body.
Understanding the anatomy and structure of bones and their different parts can help you see how the skeleton works with other parts of the body to keep you healthy and happy as a whole.